What is PXI Express?
The PXI Express (PXI-5) standard was created by the PXI Systems Alliance to integrate PCI Express advances into the PXI standard to improve performance attainable in modular instrumentation and automation systems such as those utilized by automated test developers and technicians. The PXI-Express standard brings with it several improvements but still provides a high degree of compatibility with the PXI-1 standard and compatibility with industry-standard software and operating systems. For more information on the PXI-1 standard, please follow the link to this article: What is PXI?.
Instead of a shared parallel bus, PXI Express uses multiple point-to-point serial connections (“lanes”) for instrument communication. Each lane consists of a pair of lines: one transmitting and one receiving, each able to transfer data independently allowing unimpeded bidirectional communication. A single-lane connection (‘x1’ or ‘by 1') has a bandwidth of 250 Mbytes/sec/direction. The lanes are assigned to the instruments by a matrix switch and can routed to provide one or more instruments with additional bandwidth. In this manner, devices with a higher bandwidth requirement can be allocated more resources. The PXI Express standard also incorporates a 100 MHz differential system clock that is phase-aligned with the existing 10 MHz PXI system clock and can work in conjunction with the 33MHz PCI system clock. Additional features include signaling to ensure that modules using system clocks or clock divisions are synchronized and point-to-point differential triggering. A PXI Express controller utilizes the same operating system and driver model as PXI. This ensures that the test designer can reuse existing code and software with the newer PXI Express system.
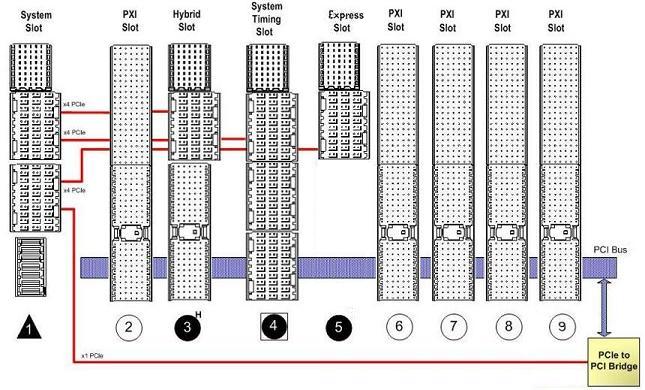
Slots
A PXI Express chassis can have five slot types:- PXI Express System Slot: slot 1 shown above
- PXI Express Peripheral Slot: slot 5 shown above
- PXI Express System Timing Slot: slot 4 shown above
- PXI Peripheral (PXI-1) Slot: slots 2 and 6 through 9 shown above
- PXI Hybrid Slot: slot 3 shown above
The PXI Express System Slot is the leftmost PXI slot, designated by a filled triangle labeled '1'. This slot will accept a system module in the form of an embedded controller or a PXI Express Bus Expander. An embedded controller is a single-board computer which comes with traditional components such as processor, memory, network and video cards, and I/O ports such as keyboard, mouse, and USB. A PXI Express Bus Expander kit allows remote control of the PXI Chassis and its hardware by another computer. The kit consists of a PXI-Express interface card which goes in the System Slot, a PCI-Express card which is installed into the desktop or plugged into the laptop, and an interface cable. If the System Module's functionality is integrated into the chassis and none is required, then the PXI System Slot will not be present on the chassis and the peripheral slot numbering will begin with '2'. Additionally, if a system module does not fit into a single slot, the PXI Express standard requires that the System Module expand to the left in slot-wide increments defined as controller expansion slots.
The System Timing Slot is intended to be used by a PXI Express System Timing Module. A System Timing Module provides individual triggers to all other PXI Express Peripheral modules and allows replacement of the system reference clock. The System Timing Module replaces the Star Trigger Module as the timing and synchronization provider for the rest of the peripheral modules. The star trigger connection points defined in PXI-1 are still retained as well as the ability to replace the system reference clock with it's own, more accurate reference clock. If a system timing module is not required, the system timing slot can be used can by a PXI Express Peripheral.
The PXI Express standard specifies that there may be slots that support PXI board as defined by the PXI Hardware Specification. These peripheral slots are referred to as PXI-1 slots. Communication with the controller is supported via an included, shared PCI bus.
Finally, there are two hybrid slots that can be used with PXI Express instruments or with legacy PXI instruments that are hybrid slot compatible.
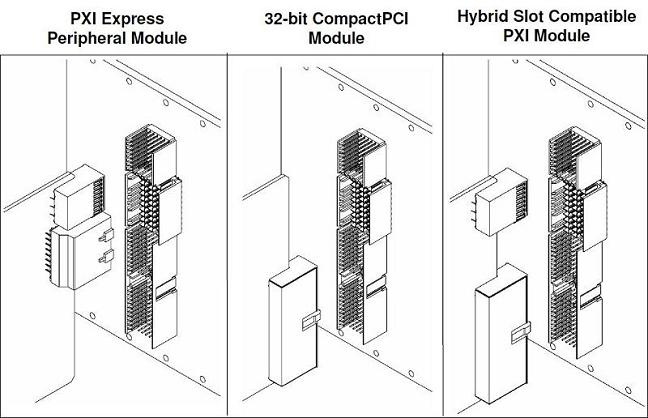
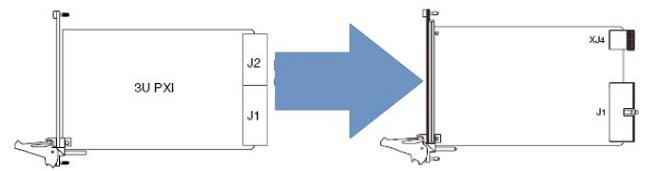
PXI-1 peripheral modules have a J1 and J2 interface to connect to the backplane. To make these instruments hybrid slot compatible, the card’s J2 interface must be removed and replaced with an XJ4 interface. The resulting interface is compatible with PXI Express chassis hybrid slots but will still work in traditional PXI-1 slots. Since removing the lower portion of the J2 interface will remove the access to the local bus, this modification should not be done on some instruments.
|
|
Keywords
|
PXI, Instrumentation, CompactPCI, PXI Express, PXIe, Standard, Defined, Hybrid, Slot, Chassis, Interface, PXI-1, Legacy
|